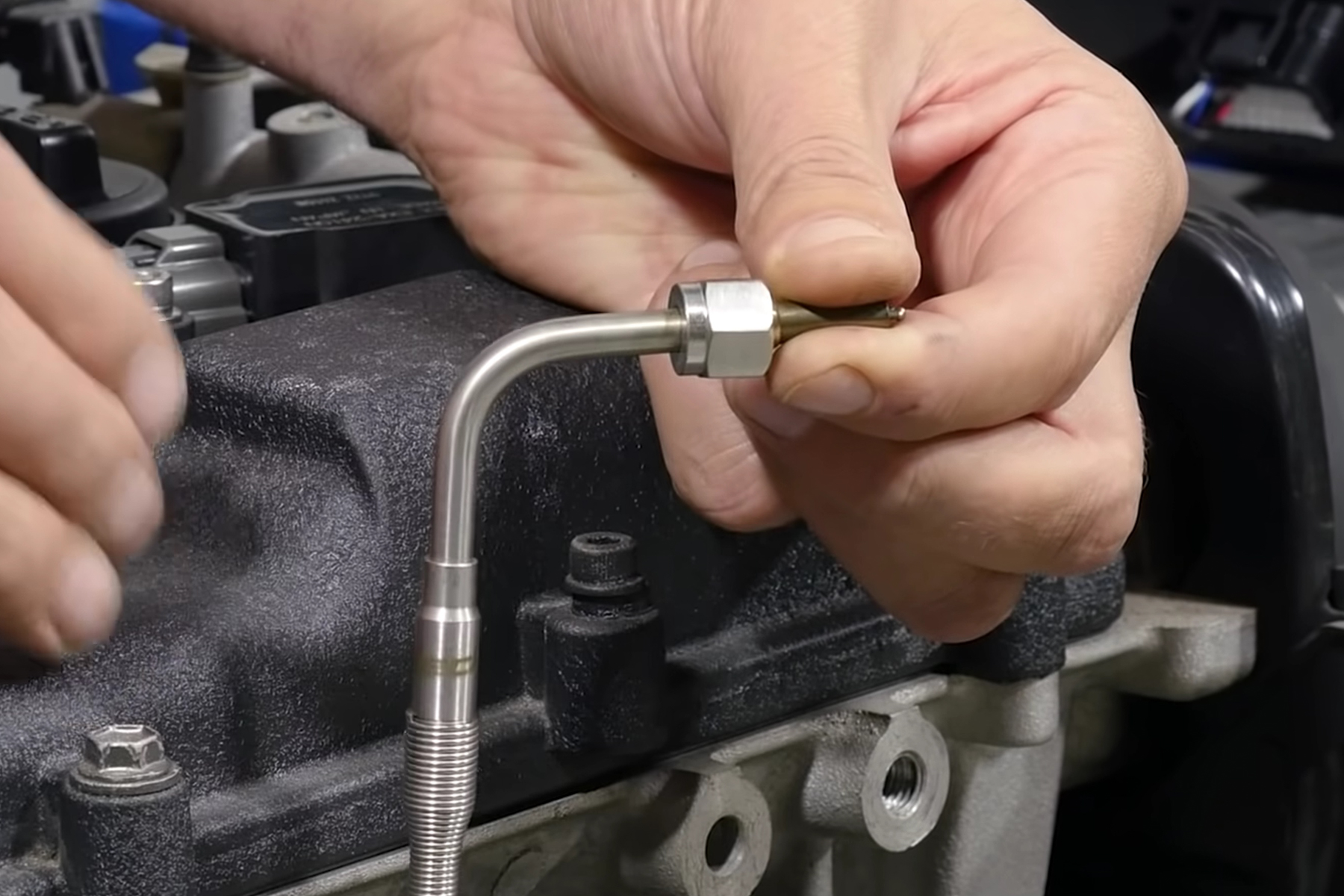
When you’re tuning an engine that’s cranking out a lot of horsepower, you need precise data to keep everything running smoothly. Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensors provide a tuner with information about each cylinder’s health. In this video, Scott from Haltech educates the world about how EGT sensors work, and how they can be used on an engine.
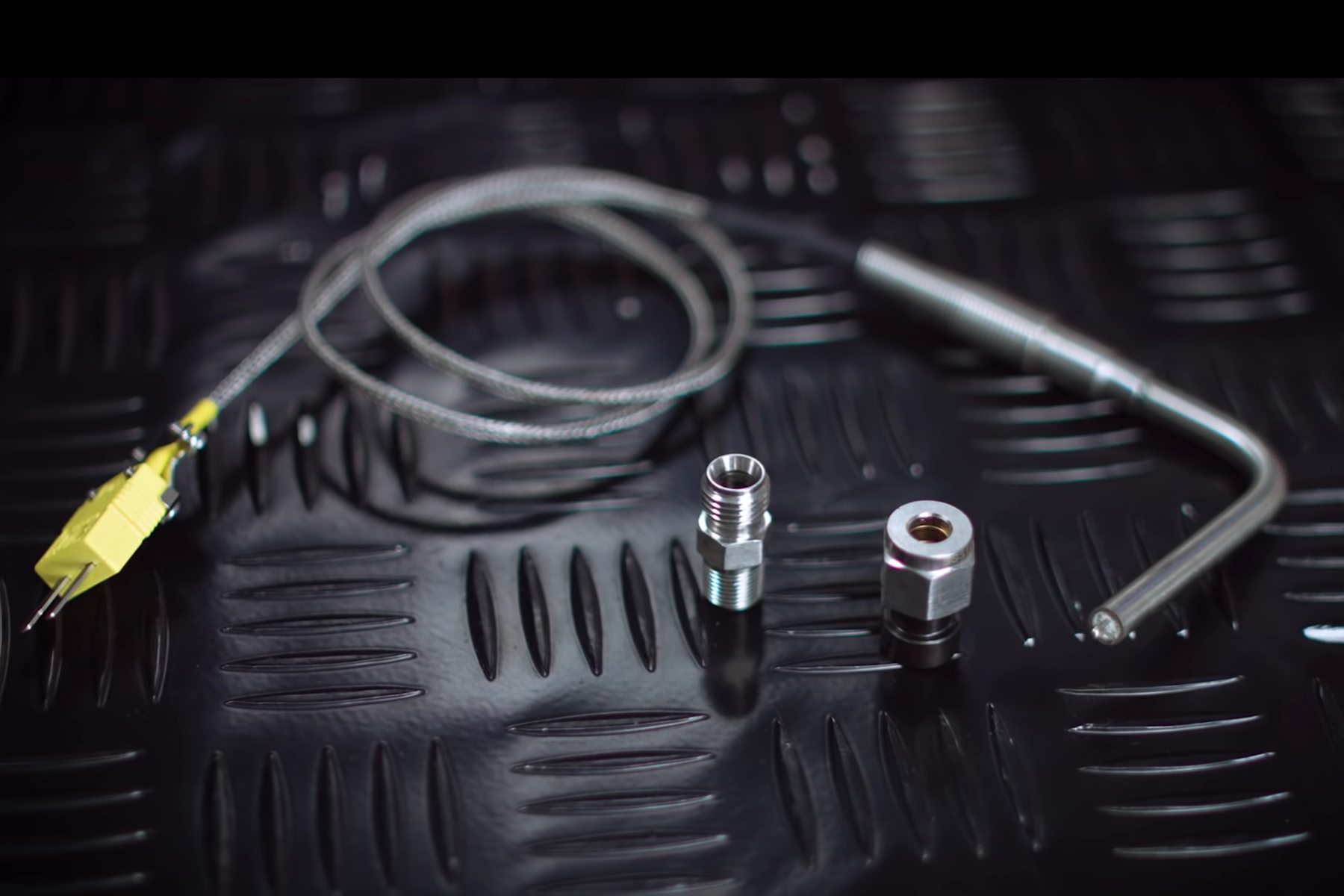
EGT sensors are essentially a thermocouple, specifically a K-type thermocouple. The K-type thermocouple can be used to measure the temperature of something in numerous applications, so it’s a very robust unit. A thermocouple measures temperatures by creating a small amount of voltage based on how the two metals that it’s made of react to temperature changes. The voltage is processed by an amplifier, and as long as the two metals that make up the sensor are known; a temperature calibration chart can be created to provide what temperature the sensor is measuring.
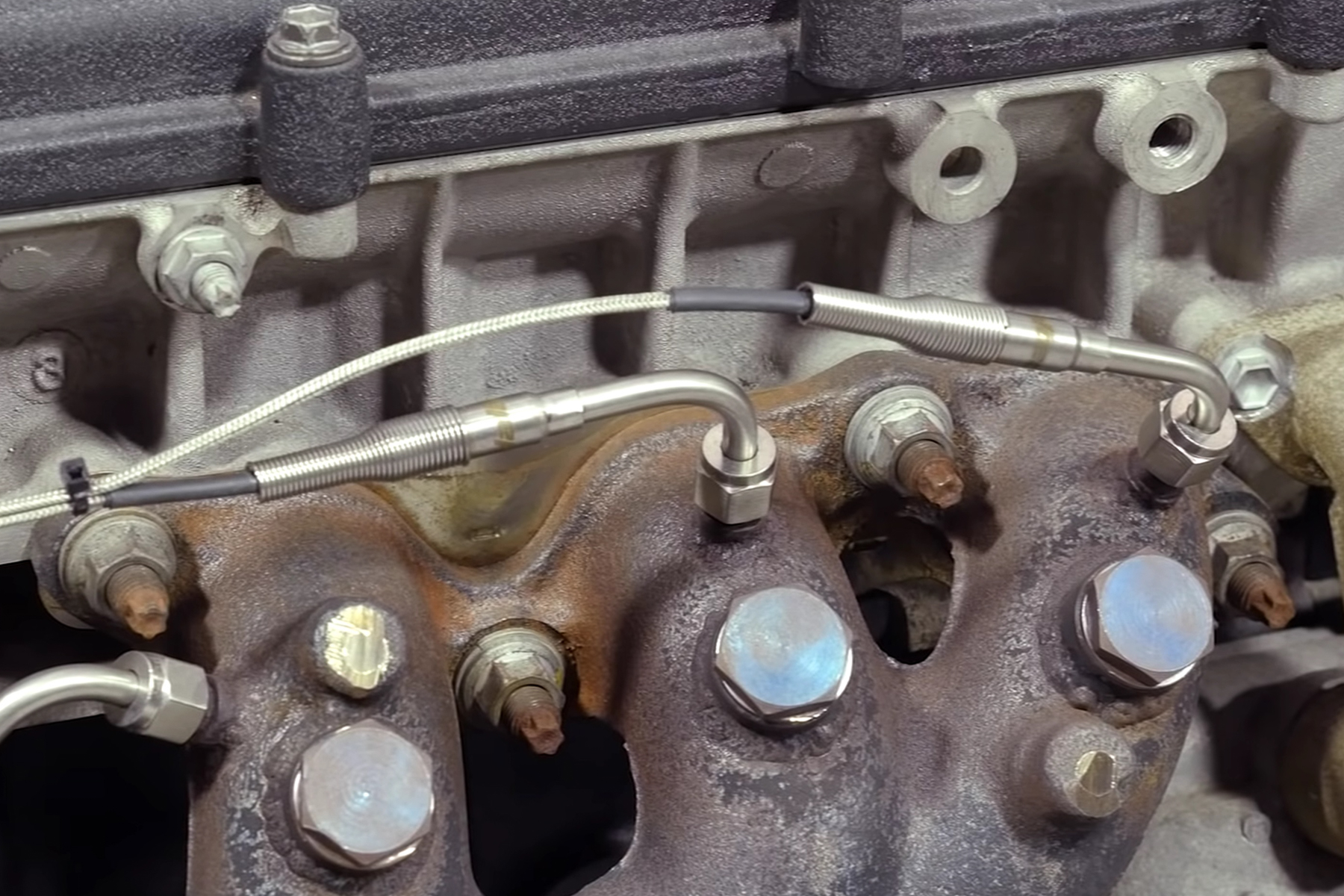
So now that you have a general idea of how an EGT sensor works, it’s time to talk about why you’d want to use one. O2 sensors are used to tune high-performance engines, but they’re usually monitoring the exhaust gasses produced by an entire bank of cylinders. That means you’re not getting precise data for each cylinder, so if one is having issues, you might not see it. Now, when you place an EGT sensor in the exhaust flow, you’ll be able to see the exact temperature for each cylinder, which correlates directly to a cylinder’s air-fuel mixture. So, if one cylinder is hotter or colder you can make fueling adjustments as needed.
Make sure you watch the video created by Haltech, it really does a great job of providing more details about EGT sensors, how they work, and why you should think about using them.